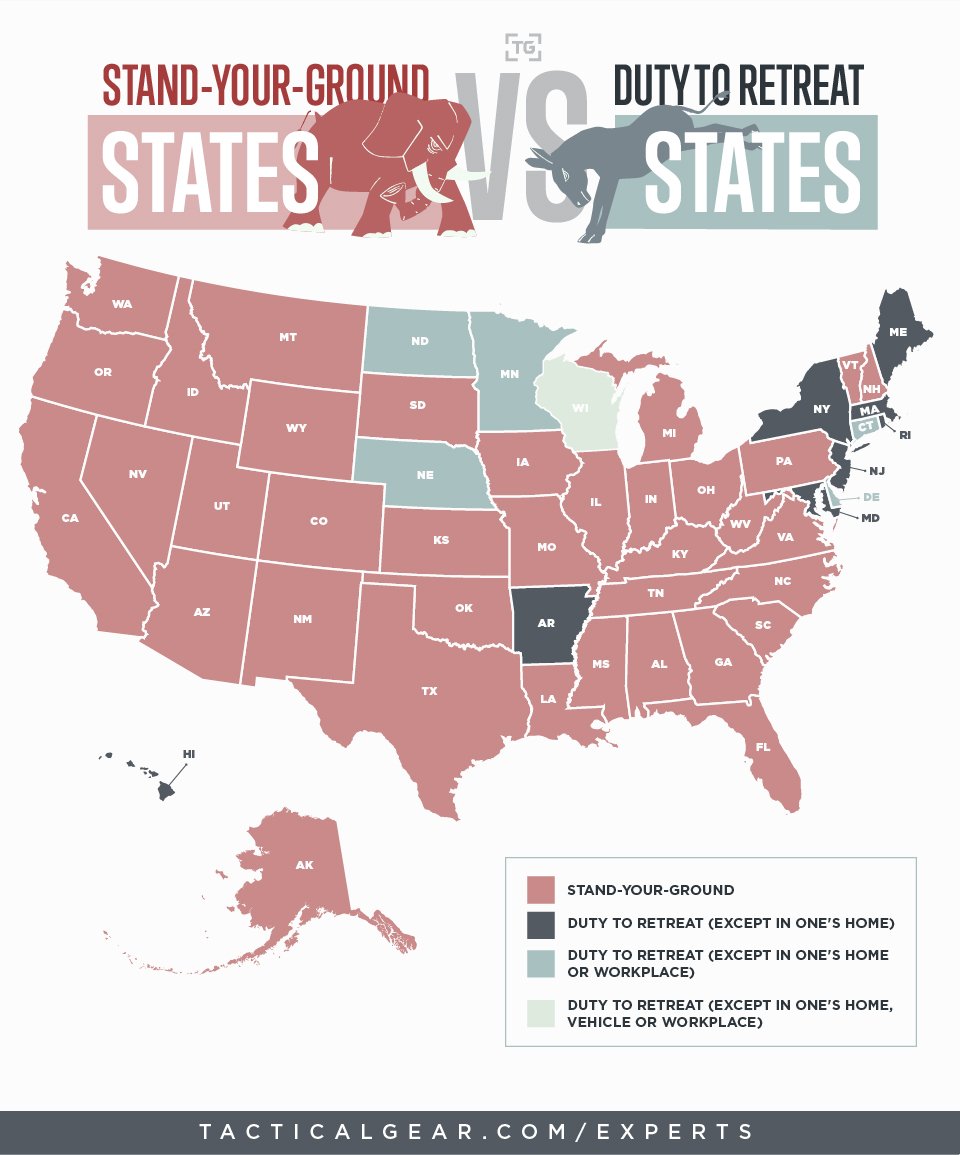
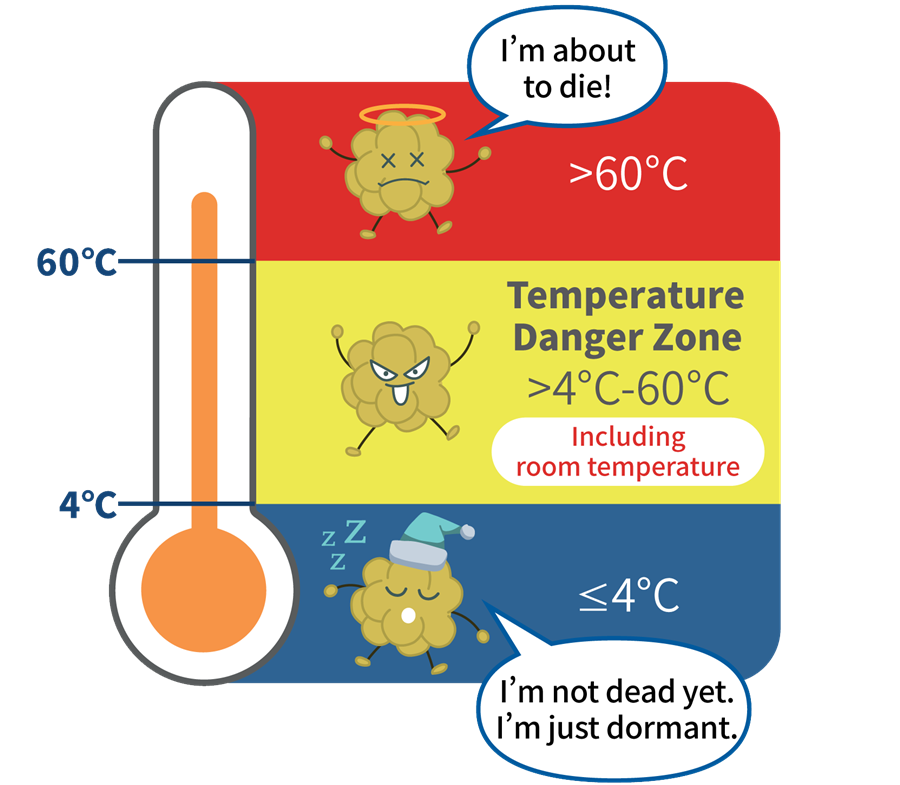
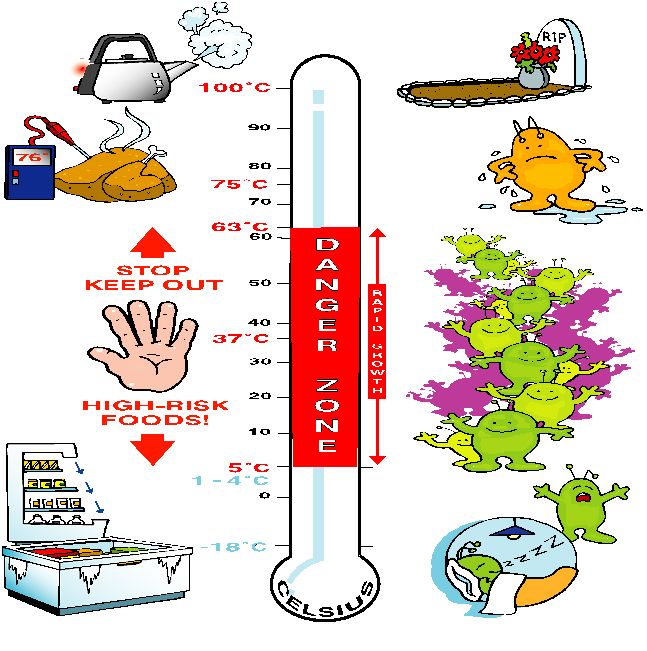
Foods that are at a temperature that allows bacteria to grow are known as the “Danger Zone.”** This zone is between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C). Bacteria grow rapidly in this temperature range, which can lead to food poisoning.
Some common foods that can be in the Danger Zone include:

- Raw meat, poultry, and seafood
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Cooked rice
- Unpasteurized milk and juices
- Sprouted seeds
- Fresh fruits and vegetables that have been cut or peeled
- Leftovers that have not been properly cooled
Bacteria can contaminate these foods at various points during production, processing, and handling. Once contaminated, the bacteria can grow and multiply rapidly if the food is not properly stored or cooked. This can lead to the production of toxins, which can cause food poisoning.
Symptoms of food poisoning can include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Muscle aches
To prevent food poisoning, it is important to follow these food safety tips:
- Keep perishable foods in the refrigerator or freezer.
- Cook raw meat, poultry, and seafood to a safe internal temperature.
- Do not leave cooked food out at room temperature for more than two hours.
- Reheat leftovers to a safe internal temperature before eating.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating them.
- Avoid unpasteurized milk and juices.
- Practice good hygiene when handling food, such as washing your hands before and after handling food and cleaning cutting boards and other surfaces after use.
By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of food poisoning.