What Are Supplies?

In the context of business and accounting, supplies refer to items that are consumed or used up in the day-to-day operations of a company. Unlike fixed assets, which are long-term investments, supplies are short-term assets that are expected to be used within one year or the company’s operating cycle, whichever is shorter. Supplies are essential for the smooth functioning of a business, and they play a crucial role in supporting various activities and processes.

Common Types of Supplies:

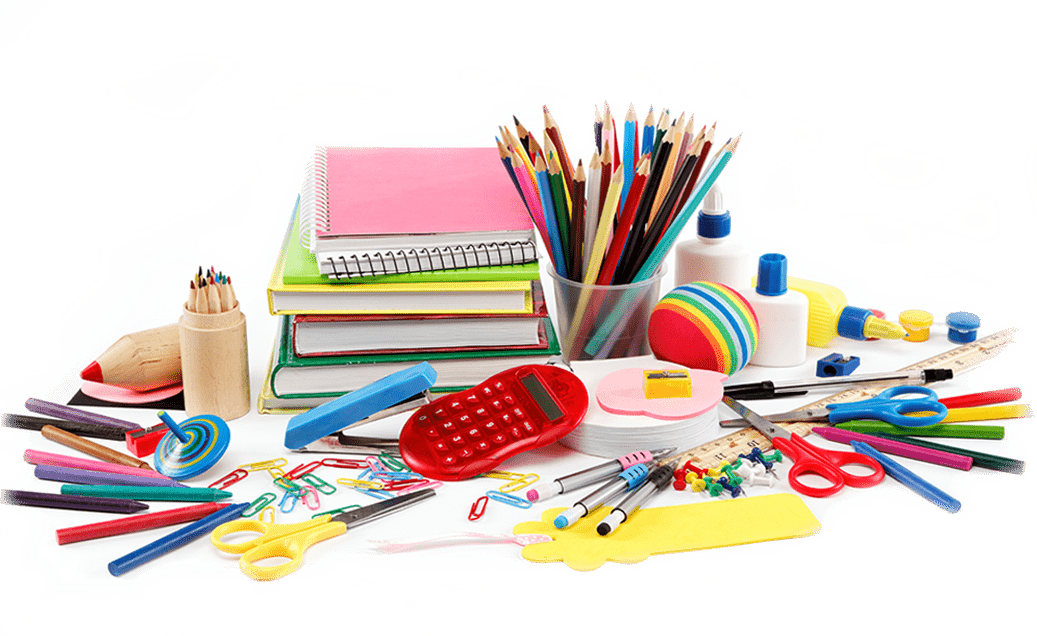
Office Supplies:
- Paper (printing, copy, note-taking, etc.)
- Pens, pencils, markers, highlighters, erasers
- Staplers, staples, paper clips, binders, folders
- Envelopes, stamps, labels, shipping materials
- Desk organizers, file folders, storage containers
- Computer peripherals (ink cartridges, toner, cables)
Janitorial Supplies:
- Cleaning agents (disinfectants, detergents, cleaners)
- Paper towels, tissues, toilet paper, hand soap
- Trash bags, garbage cans, recycling bins
- Brooms, mops, vacuums, dustpans
- Gloves, masks, safety goggles
Breakroom Supplies:
- Coffee, tea, sugar, creamer
- Disposable cups, plates, utensils, napkins
- Snacks, beverages, vending machine items
- Water cooler supplies (cups, filters, sanitizers)
- Refrigerator and microwave supplies
Tools and Equipment:
- Hand tools (hammers, screwdrivers, wrenches, pliers)
- Power tools (drills, saws, sanders, grinders)
- Safety gear (helmets, goggles, gloves, boots)
- Maintenance and repair supplies (lubricants, tapes)
Medical Supplies:
- First aid kits, bandages, antiseptic wipes
- Medications, prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs
- Medical equipment (stethoscopes, blood pressure monitors)
- Disposable gloves, masks, gowns
Importance of Supplies:
Supplies are vital for several reasons:
Operational Efficiency: Adequate supplies ensure smooth and efficient operations by providing the necessary materials and resources for various tasks.
Employee Productivity: Access to essential supplies enhances productivity by allowing employees to focus on their work without worrying about missing or inadequate resources.
Cost Control: Proper management and control of supplies help prevent wastage and overspending.
Customer Satisfaction: Having sufficient supplies ensures that customers’ needs and expectations are met promptly and effectively.
Managing Supplies:
Effective management of supplies involves:
Inventory Control: Maintaining accurate records of supplies on hand, incoming supplies, and supplies used helps prevent shortages and wastage.
Purchasing: Careful planning and negotiation with suppliers can result in cost savings and ensure timely delivery of supplies.
Storage: Organizing and storing supplies properly maximizes storage space, minimizes damage, and facilitates easy access.
Asset Tracking: Assigning unique identifiers to expensive or critical supplies helps monitor their usage and prevent theft.
Expense Control: Establishing clear policies and procedures for supply usage and disposal minimizes unnecessary or unauthorized spending.
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with reliable suppliers ensures consistent quality, competitive pricing, and timely deliveries.
Supplies play a crucial role in the daily functioning of a business. By effectively managing supplies, businesses can optimize costs, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure customer satisfaction.