Food manufacturing encompasses the processes of transforming raw agricultural ingredients into consumable food products. It involves a series of operations, including harvesting, processing, packaging, and distributing food items. The primary objective of food manufacturing is to provide safe, nutritious, and appealing food products to consumers while ensuring food safety and quality standards.

The food manufacturing industry plays a vital role in the global food supply chain, catering to the diverse dietary needs and preferences of individuals. Various techniques and technologies are employed to convert raw materials into a wide range of food products, including beverages, baked goods, canned goods, dairy products, frozen foods, snacks, and processed meats.
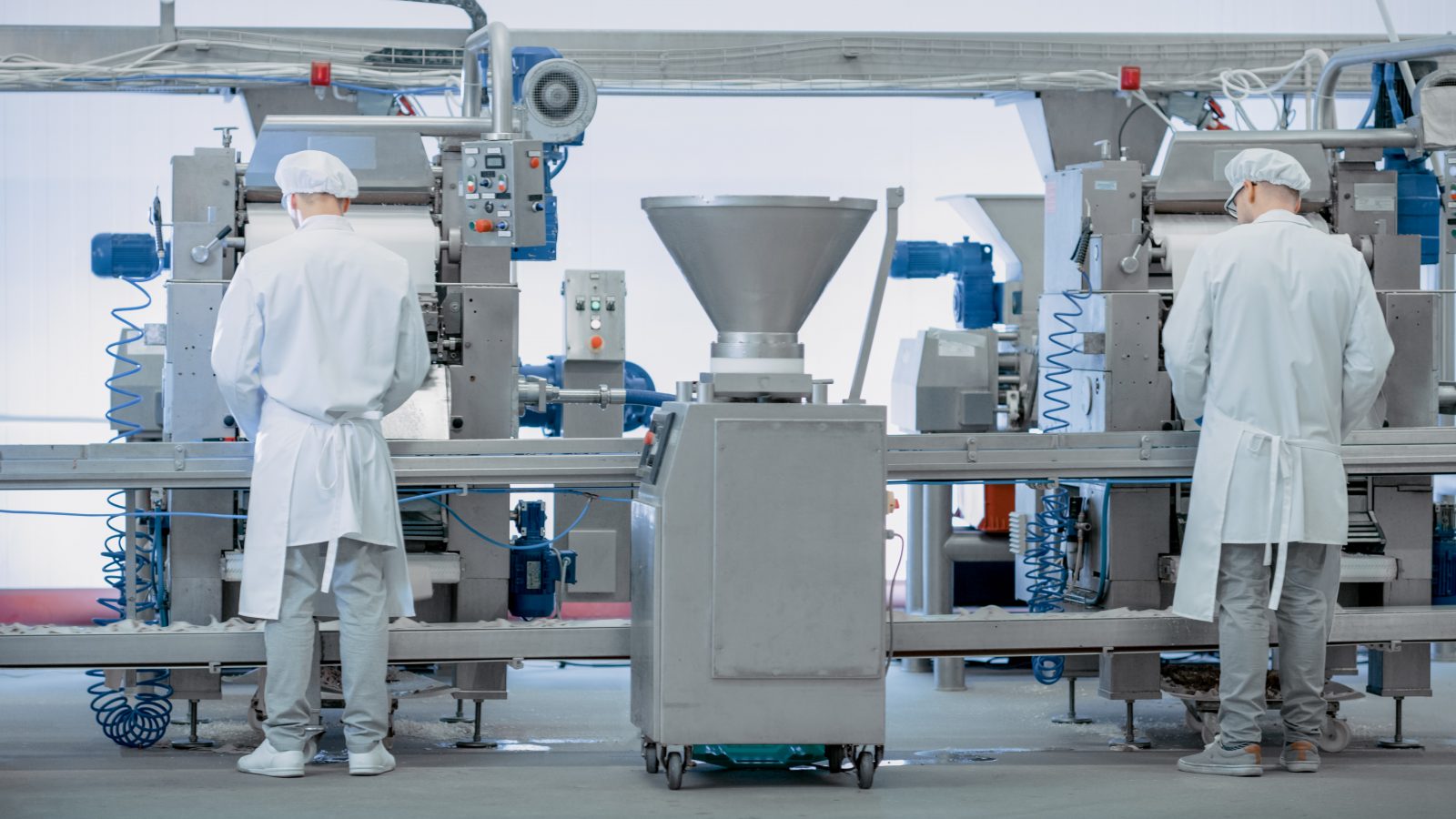

Key stages in food manufacturing include:

Harvesting and Sourcing: The process begins with harvesting raw ingredients, such as grains, fruits, vegetables, livestock, and seafood, from farms, orchards, ranches, and fisheries. These ingredients are carefully selected to meet specific quality criteria.
Pre-processing: Before further processing, raw ingredients undergo pre-processing steps to prepare them for subsequent operations. This may involve activities like cleaning, sorting, grading, washing, and cutting to ensure consistency and remove unwanted materials.
Processing: The core of food manufacturing involves processing raw ingredients into consumable products. Various processing methods are utilized, depending on the type of food being manufactured. Some common techniques include cooking, baking, milling, grinding, freezing, dehydration, fermentation, and pasteurization. These processes transform the ingredients into desired flavors, textures, and nutritional compositions.
Packaging: Processed food items are then packaged to protect them from spoilage, contamination, and physical damage during storage, transportation, and handling. Packaging materials, such as cans, bottles, bags, and boxes, are carefully chosen to maintain product quality and extend shelf life.
Quality Control and Assurance: Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control and assurance measures are implemented to ensure food safety and compliance with regulatory standards. This involves testing, inspecting, and monitoring food products at various stages to identify and address potential hazards or deviations from established specifications.
Storage and Distribution: Once packaged, food products are stored in controlled environments, such as warehouses or distribution centers, to maintain their quality until they are ready for distribution. Efficient logistics and supply chain management systems ensure timely and cost-effective delivery of food products to retail outlets, restaurants, and other distribution channels.
Food manufacturing is a dynamic and continuously evolving industry, driven by consumer demands, technological advancements, and the need for sustainable and environmentally conscious practices. It plays a crucial role in meeting the growing global food demand and providing consumers with a diverse range of safe, nutritious, and affordable food products.