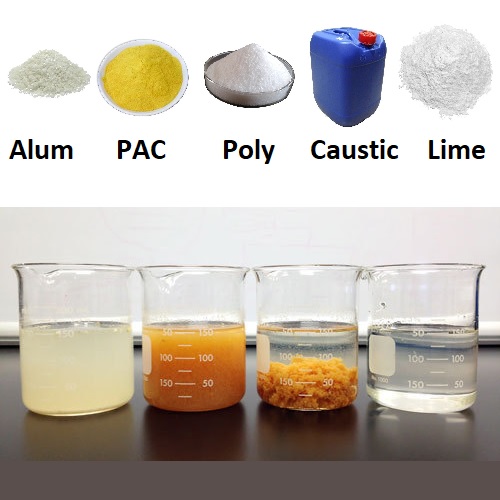
Chemicals Used in Water Treatment:

1. Coagulants:
Coagulants are chemicals that help to destabilize and aggregate suspended particles in water, making them easier to remove. Common coagulants include:
- Alum (Aluminum Sulfate): Alum is a widely used coagulant that forms positively charged aluminum hydroxide flocs that neutralize the negative charges of suspended particles, causing them to clump together.
- Ferric Chloride: Ferric chloride is another common coagulant that forms positively charged iron hydroxide flocs. It is often used in conjunction with alum to improve coagulation efficiency.
- Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC): PAC is a highly effective coagulant that forms positively charged aluminum hydroxide flocs. It is often used in water treatment plants that require high-quality water.
2. Flocculants:
Flocculants are chemicals that help to bind together and enlarge the coagulated particles, forming larger and heavier flocs. Common flocculants include:
- Polyacrylamide: Polyacrylamide is a synthetic organic polymer that is commonly used as a flocculant. It is available in various molecular weights and can be tailored to suit specific water treatment applications.
- Natural Polymers: Natural polymers, such as guar gum and starch, can also be used as flocculants. They are typically less expensive than synthetic polymers but may be less effective in certain applications.
3. Disinfectants:
Disinfectants are chemicals that kill or inactivate microorganisms in water, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. Common disinfectants include:
- Chlorine: Chlorine is a widely used disinfectant that is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms. It is typically added to water in the form of chlorine gas or sodium hypochlorite solution.
- Chloramines: Chloramines are formed by the reaction of chlorine and ammonia. They are less corrosive than chlorine and provide longer-lasting disinfection.
- Ozone: Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent that is effective against a wide range of microorganisms. It is typically generated on-site using oxygen gas.
4. pH Adjusters:
pH adjusters are chemicals that are used to adjust the pH of water to an optimal level for coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection processes. Common pH adjusters include:
- Sodium Hydroxide: Sodium hydroxide is a strong base that is used to increase the pH of water.
- Sulfuric Acid: Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that is used to decrease the pH of water.
5. Corrosion Inhibitors:
Corrosion inhibitors are chemicals that are added to water to prevent or reduce corrosion of metal pipes and equipment. Common corrosion inhibitors include:
- Polyphosphates: Polyphosphates form a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing corrosion.
- Silicates: Silicates also form a protective layer on metal surfaces, preventing corrosion.
The specific chemicals used in water treatment vary depending on the source water quality, desired water quality, and treatment processes employed. The selection and dosage of chemicals are typically determined through laboratory testing and pilot studies.