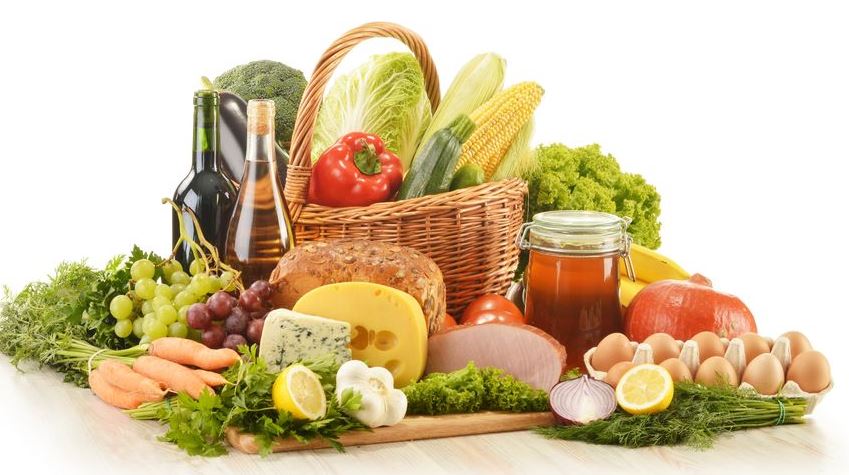
Increased Nutritional Value: Homegrown produce often has higher nutritional content compared to store-bought options. By controlling the growing conditions, such as soil quality, sunlight exposure, and water usage, you can optimize the nutrient density of your food. This results in fruits, vegetables, and herbs that are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients, promoting overall health and well-being.

Better Taste and Quality: Homegrown food simply tastes better. When produce is picked at its peak ripeness and consumed fresh, it retains its natural flavors and aromas. Store-bought produce, on the other hand, is often picked before it reaches full maturity and may lose flavor and nutrients during transportation and storage. Growing your own food allows you to experience the true taste of fresh, flavorful produce, making meals more enjoyable and satisfying.

Control Over Growing Practices: Growing your own food gives you complete control over the growing practices used. You can choose organic methods, evitando the use of pesticides, herbicides, and synthetic fertilizers. This ensures that you and your family are consuming food free from harmful chemicals. Additionally, you can cater to specific dietary preferences or health concerns by selecting varieties that are low in certain allergens or high in particular nutrients.

Cost Savings: Growing your own food can be a cost-effective way to feed your family. While the initial investment in seeds, soil, and containers may seem substantial, the long-term savings can be significant. Homegrown produce can supplement or even replace store-bought items, reducing your grocery budget. Furthermore, growing your own food can be a rewarding hobby that provides fresh, healthy produce at a fraction of the cost of organic produce from the market.
Environmental Sustainability: Growing your own food promotes environmental sustainability. By reducing the demand for commercially produced food, you contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions associated with transportation, food processing, and packaging. Additionally, homegrown food often requires less water and energy compared to conventionally grown crops. Furthermore, organic gardening practices can improve soil health and biodiversity, benefiting the local ecosystem.
Educational Opportunities: Growing your own food can serve as an educational opportunity for children and adults alike. It teaches valuable lessons about nature, ecology, and the importance of sustainable agriculture. By actively participating in the growing process, individuals can develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for where their food comes from. This knowledge can foster healthier eating habits and a greater connection to the natural world.
What Are The Benefits Of Growing Your Own Food