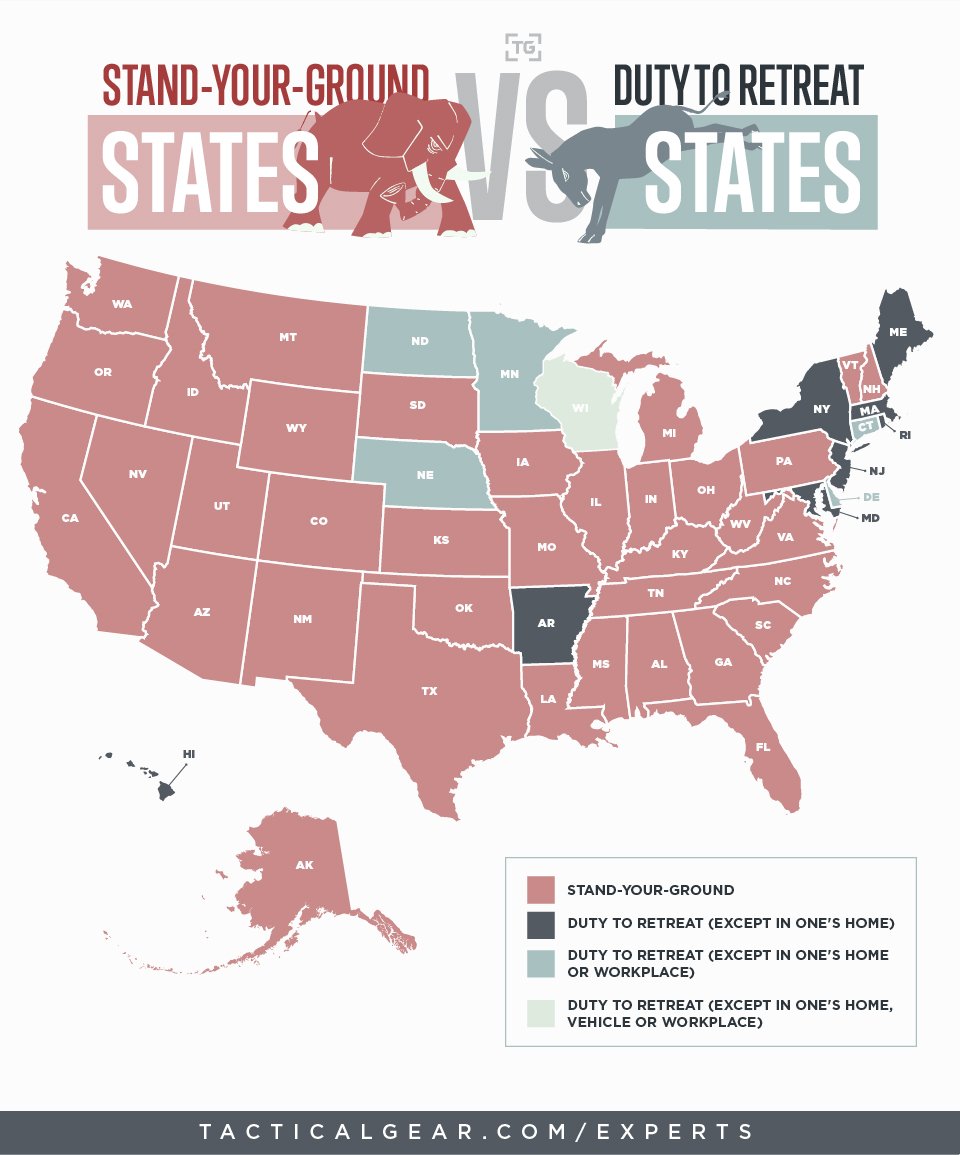
Enhancing the infrastructure of storage facilities for food products greatly contributes to the sustainability of farming practices in several ways:

Reduced Post-Harvest Losses:

Inefficient storage facilities can lead to significant post-harvest losses due to factors like improper temperature and humidity control, pest infestations, and inadequate protection from external elements. By upgrading storage facilities, farmers can minimize these losses, ensuring that a greater proportion of harvested crops reach consumers while preserving their quality. This directly impacts the economic viability of farming by reducing waste and increasing the value of produce.
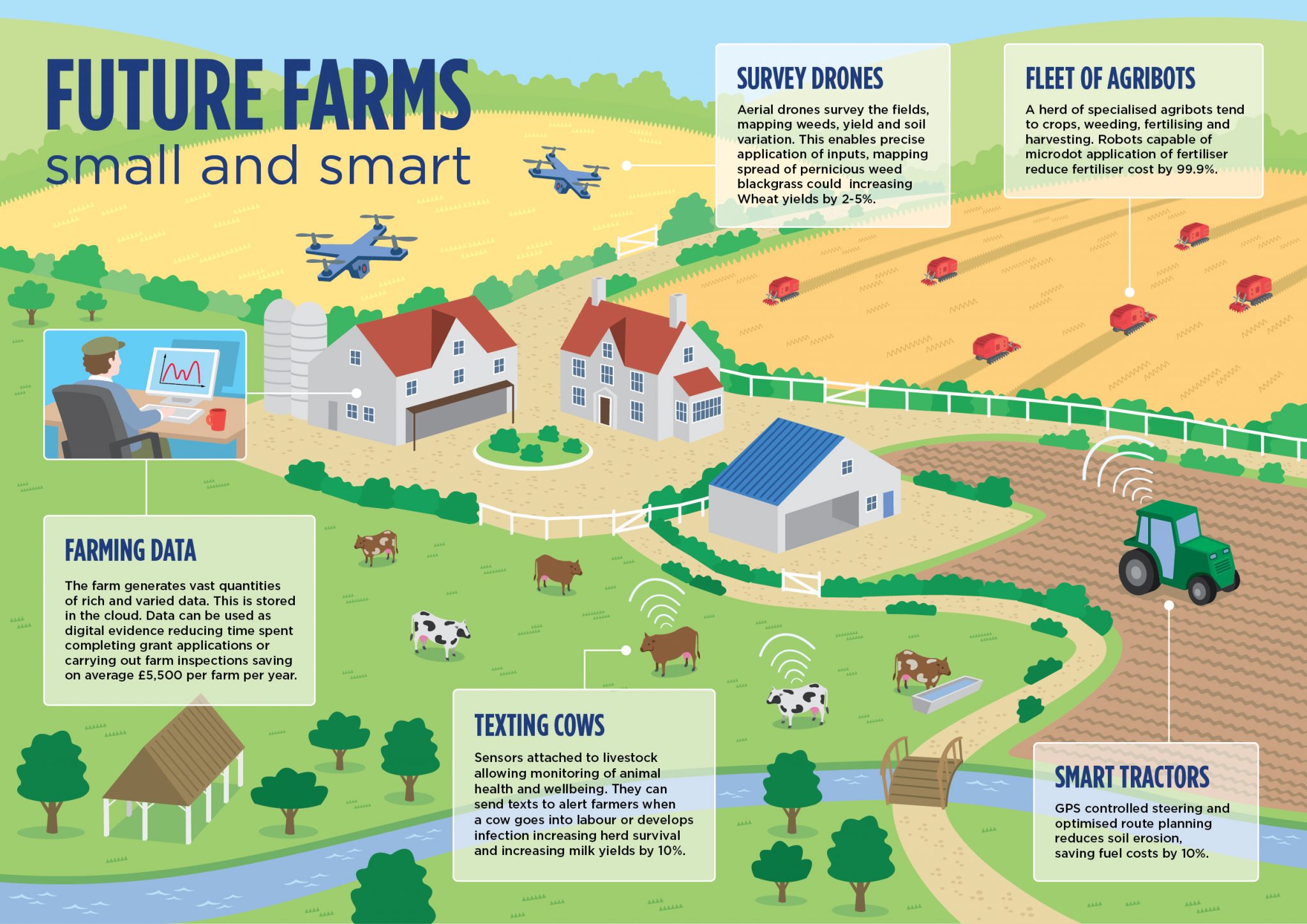
Extended Shelf Life:
Proper storage conditions allow farmers to extend the shelf life of their produce, maintaining its freshness and quality for a longer duration. This enables farmers to plan their sales and marketing strategies more effectively, reducing the risk of spoilage and maximizing profits. Extended shelf life also provides flexibility in managing supply and demand, allowing farmers to respond to market fluctuations and changing consumer preferences.
Improved Food Quality:
Adequate storage facilities preserve the nutritional value, flavor, and overall quality of agricultural produce. Maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels prevents spoilage and deterioration, ensuring that consumers have access to high-quality food products. This, in turn, enhances the reputation and market value of the farm’s produce, increasing consumer confidence and potentially fetching higher prices.
Year-Round Availability:
Efficient storage facilities enable farmers to regulate the supply of their products throughout the year, even during off-season periods. This helps stabilize market prices, reducing price fluctuations and ensuring a steady income for farmers. Additionally, consumers benefit from year-round access to a diverse variety of fresh and high-quality produce, promoting healthier and more diverse diets.
Increased Market Opportunities:
Improved storage facilities allow farmers to expand their market reach by transporting their produce over longer distances and accessing new markets that were previously inaccessible due to limited storage capacity or product deterioration during transit. This diversification of markets reduces the reliance on local demand and enhances the resilience of farming operations.
Environmental Sustainability:
Reducing post-harvest losses and extending the shelf life of produce can significantly reduce the environmental impact of farming. By minimizing the need for additional production to compensate for lost or spoiled crops, farmers can conserve resources like water, energy, and land. Efficient storage facilities also contribute to reducing food waste, which is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
By investing in improving food storage facilities, farmers can optimize their operations, enhance the quality and availability of their produce, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system.