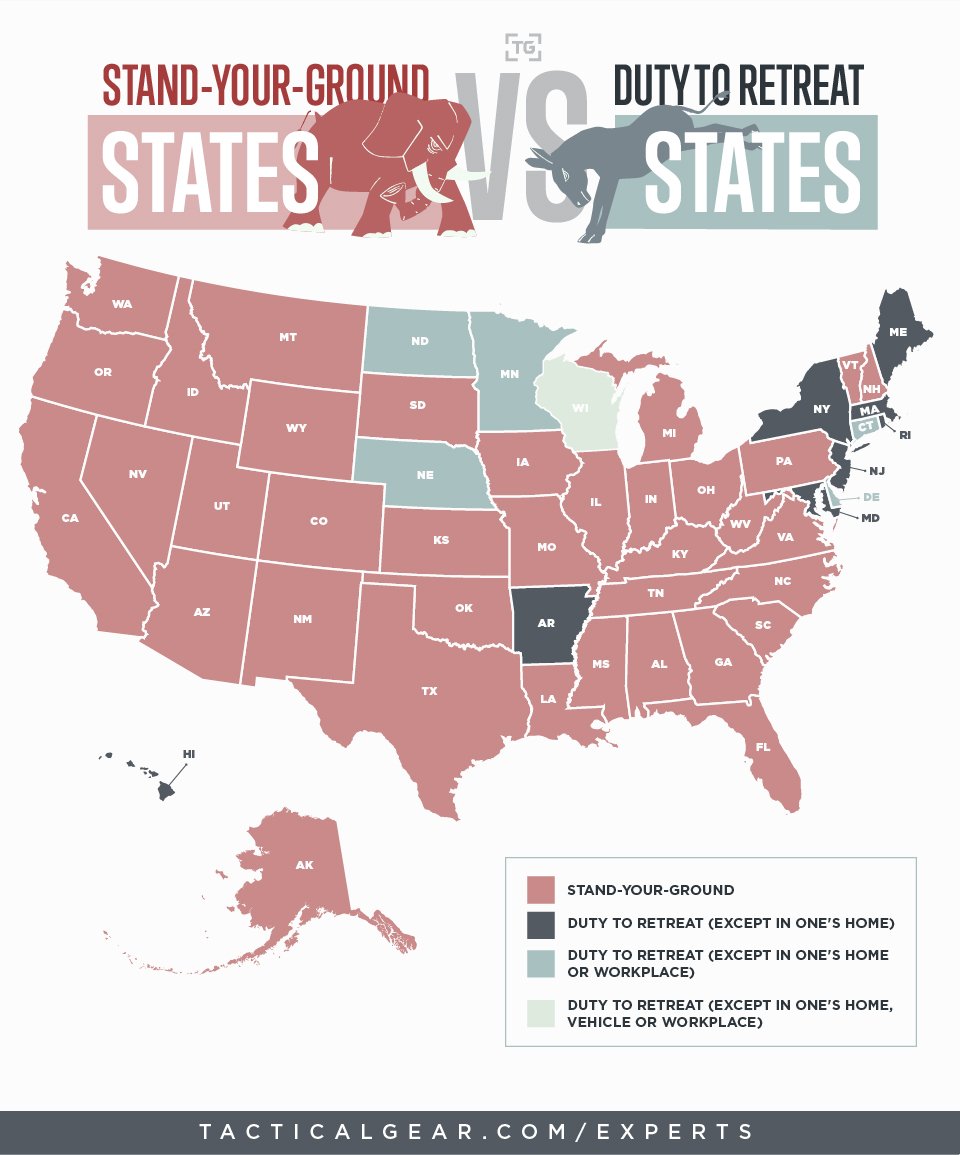
Choose the Right Location:

Select a spot with plenty of sunlight, as most fruits require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can harm the roots.

Consider factors like wind protection, especially for taller trees.
Prepare the Soil:
Test your soil’s pH and amend it if necessary. Most fruits prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8.
Add organic matter, like compost or manure, to improve soil fertility and structure.
Make sure the soil is loose and well-drained to allow proper root development.
Choose the Right Fruit Trees or Plants:
Select varieties suitable for your climate and growing conditions. Consider factors like hardiness zone, ripening time, pest and disease resistance, and desired fruit size and taste.
Purchase healthy, disease-free plants from a reputable nursery.
Planting:
Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball of the plant.
Place the plant in the hole, ensuring the graft union (where the rootstock and scion are joined) is above the soil line.
Backfill the hole with soil and gently tamp down to remove air pockets.
Water thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots.
Watering and Fertilizing:
Water regularly, especially during dry spells. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Fertilize according to the specific needs of the fruit tree or plant. Use balanced fertilizers and follow the recommended application rates.
Pruning:
Prune fruit trees and plants regularly to maintain a healthy structure and promote fruiting.
Different fruits have different pruning requirements, so research the specific needs of your variety.
Pruning helps control tree size, remove dead or diseased branches, and encourage new growth.
Pest and Disease Management:
Monitor your fruit trees and plants for signs of pests or diseases.
Use appropriate pest control methods, such as organic pesticides or neem oil, if necessary.
Employ disease prevention strategies like proper watering, sanitation, and avoiding overcrowding.
Harvesting:
Harvest fruits when they are ripe. Timing varies depending on the fruit variety and local climate.
Carefully pick the fruits by hand, avoiding damage to the skin.
Store the harvested fruits properly to maintain their quality and freshness.
How Do You Grow Fruit