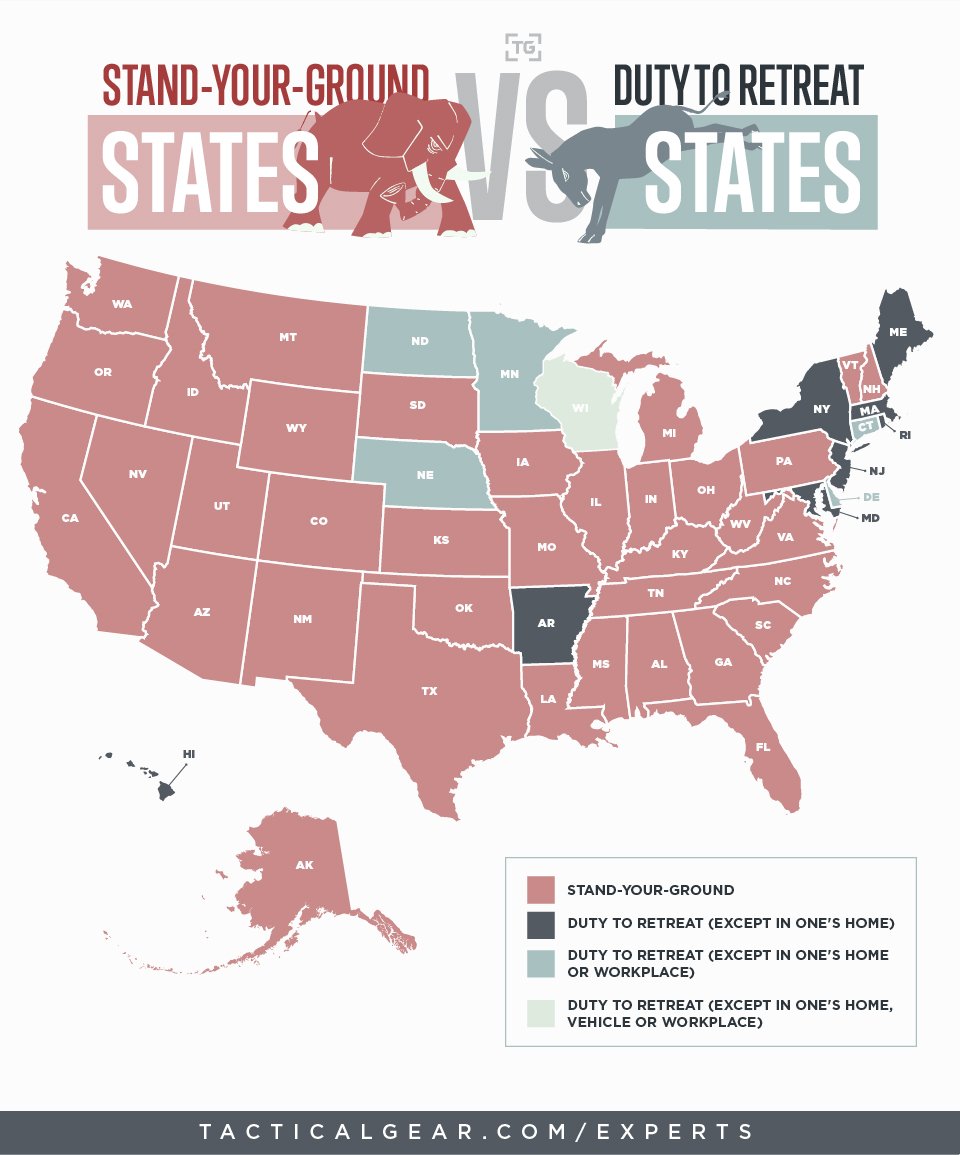
Coagulation and Flocculation
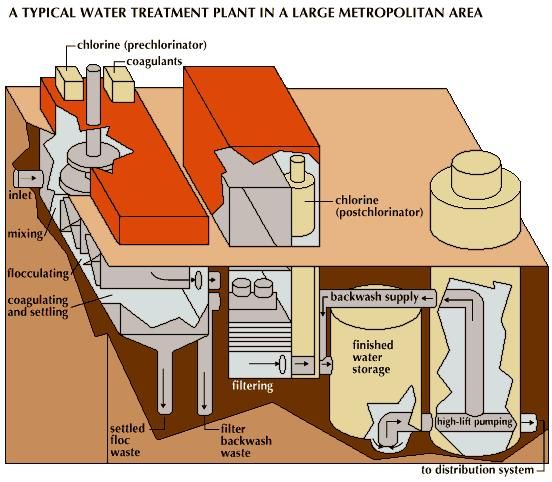
The first step in water purification is typically coagulation and flocculation. During coagulation, small positively charged ions are added to the water and attract negatively charged particles and pathogens in the water. This causes the particles to bind together and form larger particles called flocs.
Flocculation
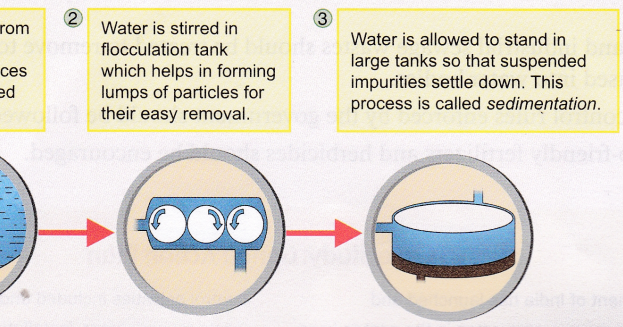
The second step is flocculation, which involves adding chemicals to the water, such as aluminum sulfate or ferrous sulfate. These chemicals cause the flocs to become larger and heavier, making them easier to remove.
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the process of allowing the flocs to settle to the bottom of a tank. Clean water is then removed from the top of the tank, while the settled solids are removed and disposed of.
Filtration
The fourth step is filtration. During filtration, the water is passed through a porous material, such as sand and gravel, or through a membrane. This removes any remaining particles or contaminants from the water.
Disinfection
The final step in water purification is disinfection. During disinfection, chemicals such as chlorine and chloramine are added to the water to kill bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms that may be present. Other methods of disinfection include ultraviolet light and ozonation, but chlorination is the most common method, especially for large municipal systems.
Finally, the water is tested to ensure that it meets regulatory requirements for drinking water quality.
It is important to note that the specific steps involved in water purification can vary depending on the quality of the raw water and the desired quality of the finished water.